Description
The earth horizon sensor module is an image processing algorithm that calculates the pitch and roll error of the current sensor’s view with the earth’s horizon, relative to that sensor’s orientation on the Spacecraft.
Module Implementation
This module was implemented with a few known variables in mind to achieve the same result the sensor’s algorithm would try to perform on its thermal image data:
- The current earth’s radius
- The current earth’s position (in inertial space)
- The current sensor’s position (in inertial space)
- The current sensor’s rotation (DCM in inertial space)
With this information in mind, there are 4 stages that we need to perform:
1) Calculate horizon point DCM from the sensor’s view
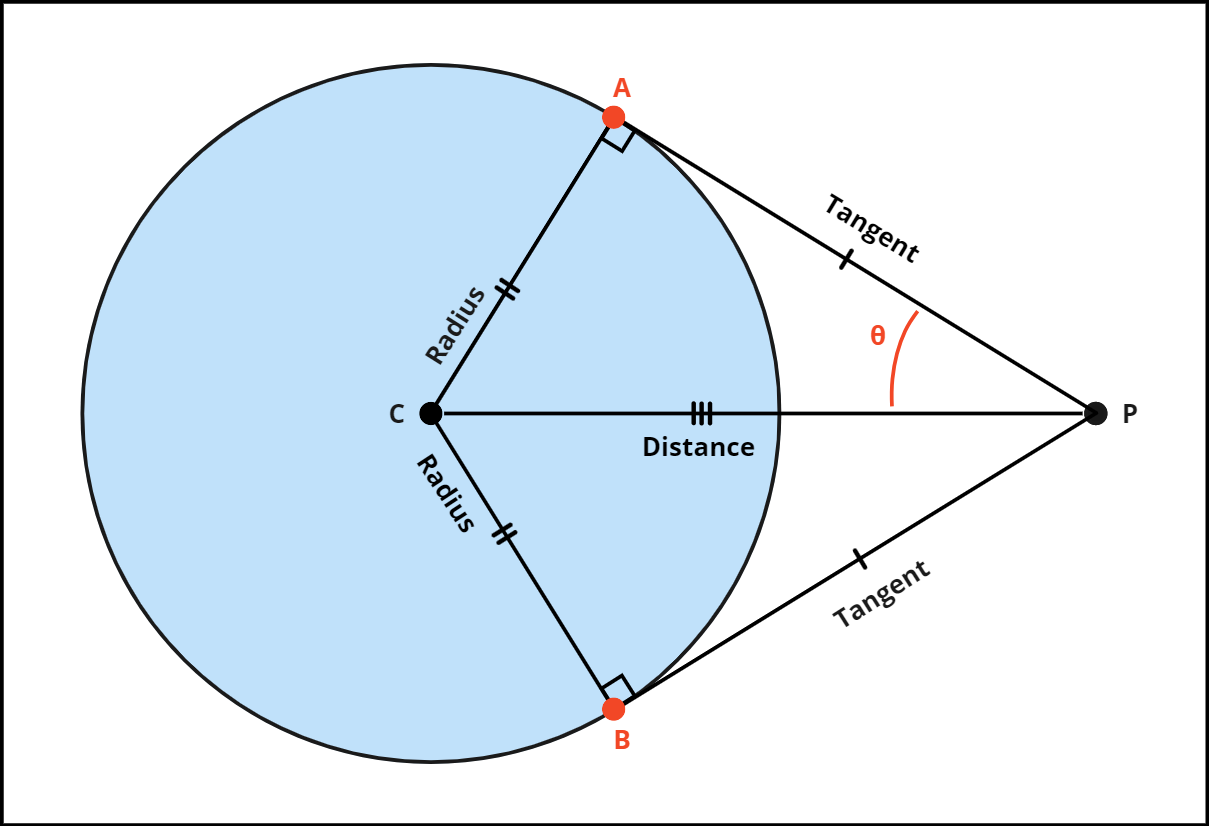
We can use the Two-Tangent Theorem to calculate the closest horizon point from sensor P. Because we are dealing with 3D coordinates we needed to take a different approach. We already know the Radius of the earth and we can also calculate the Distance of the sensor to planet C, therefore we can calculate the angle θ using arcsin. The next step is to calculate a DCM matrix using the normalized direction of → and the sensor’s forward vector. Finally, we can use the angle to pitch the DCM up and down to give us the horizon points A and B, which then we use the dot product to give us the closest horizon point and horizon point DCM.
To calculate the θ angle:
To calculate the DCM matrix:
To calculate the horizon A point:
To calculate the horizon B point:
To calculate the closest horizon point H:
To calculate the horizon point DCM matrix HR:
- where projects the point
Pinto an infinite plane with an offsetOand a normalN - where projects a ray point
Pand directionDinto an infinite plane with an offsetOand a normalN
2) Calculate roll error from the sensor’s DCM with the horizon’s DCM
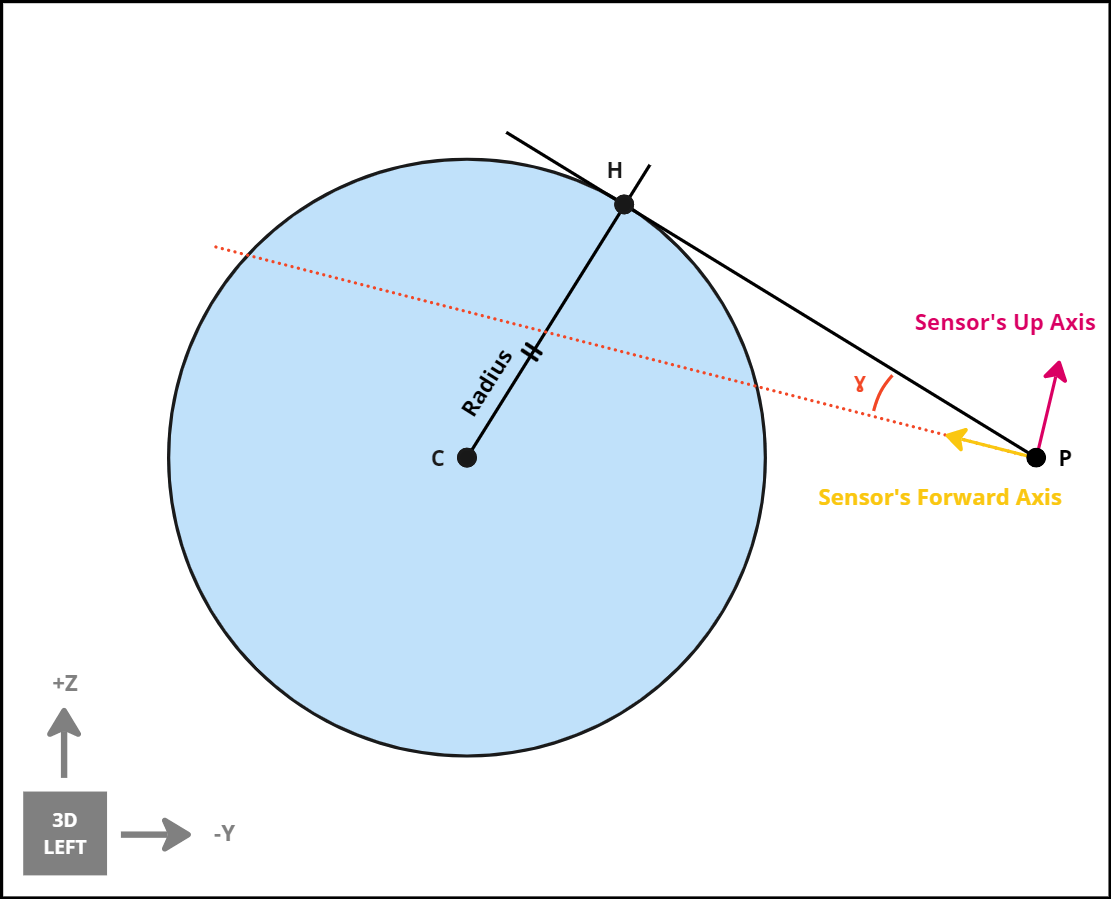
The roll-error is the angle between the Right axis of the sensor and the corresponding axis of the horizon point DCM
The direction of the roll is determined using the dot product between the right axis of the sensor and the up axis of the horizon point
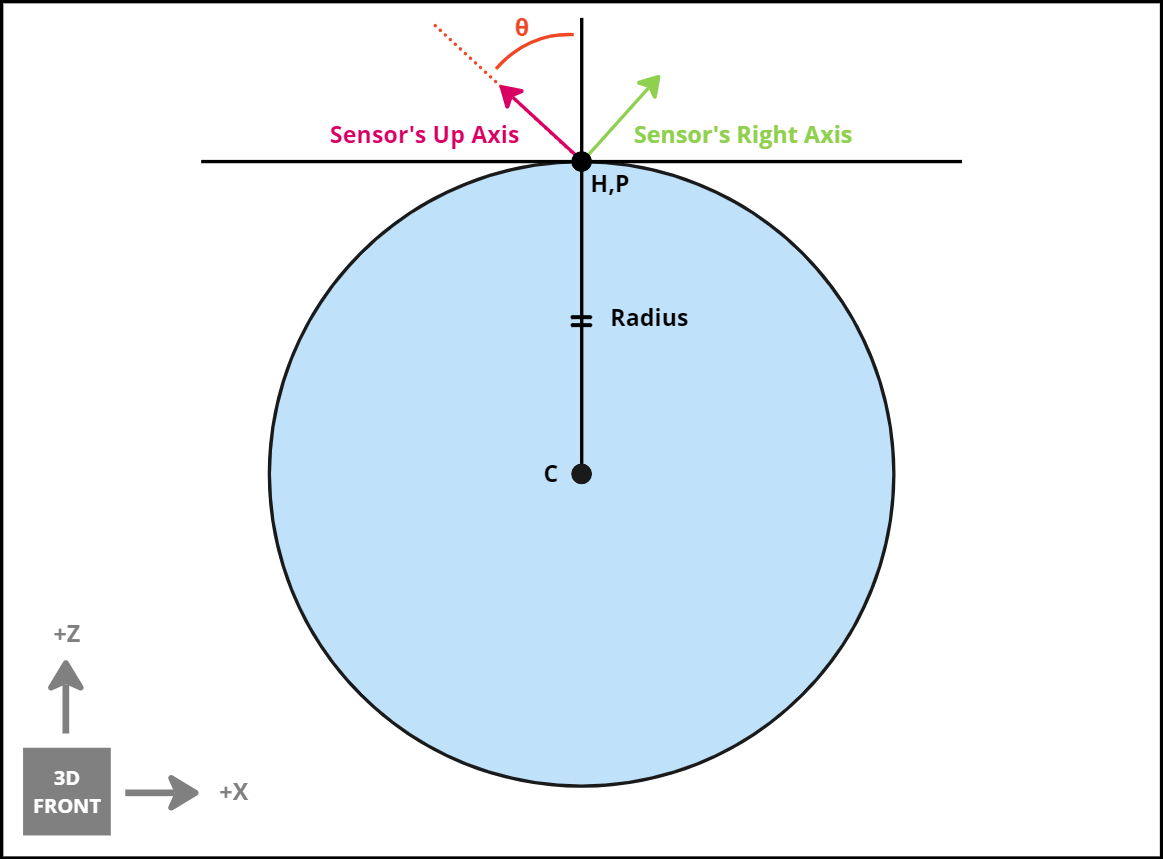
3) Calculate pitch error from the sensor’s DCM with the horizon’s DCM
The pitch error is the angle between the forward axis of the sensor and the up axis of the horizon point DCM
The direction of the roll is determined using the dot product between the forward axis of the sensor and the forward axis of the horizon point
Assumptions/Limitations
This sensor acts as a “perfect” sensor, meaning it can accurately calculate the position of the horizon line without having to perform any real image processing algorithm to achieve the result.