Description
As illustrated below, the purpose of this module is to act as an analogue to the digital interface for the generation of Reaction Wheel telemetry. It implements three different encoder models:
- Nominal: Discretized reaction wheel speed information is read.
- Stuck: Reaction wheel speed information is not updated and is “stuck” at the last read state.
- Off: No reaction wheel speed information is read. A value set to zero.
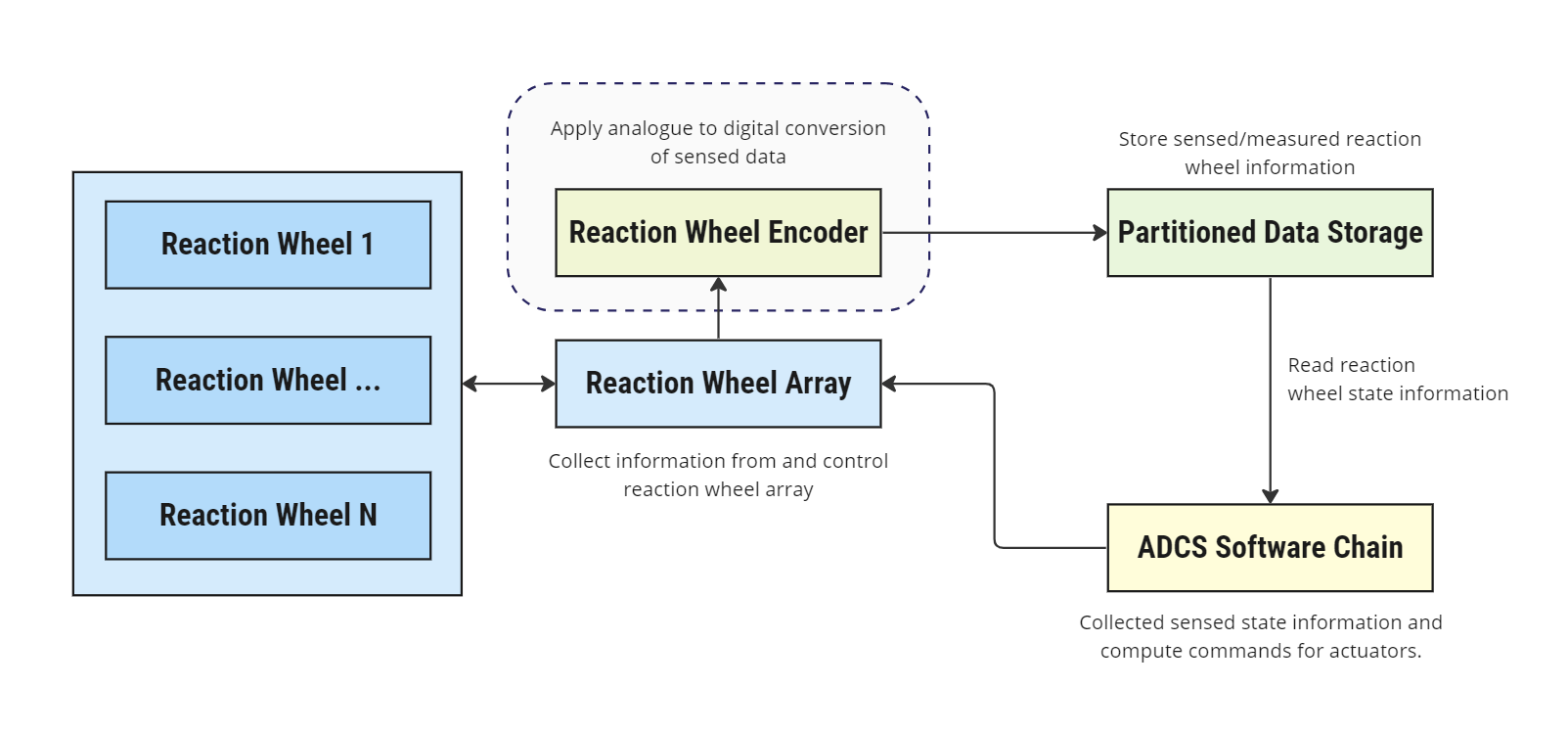
This information may be stored in a local data cache, as in Figure 1, or passed directly to a consumer of this data e.g. directly to the ADCS software chain in Figure 1. The former is a more realistic data flow.
Example Use Cases
- Analysis of the impact of RW sensor resolution on point budgets: By applying a discretization error to reaction wheel speeds, this model allows the user to consider the impact of RW sensor resolution of pointing stability as imperfect knowledge of RW states will influence command torques.
Module Implementation
Discretization errors are applied to the reaction wheel speed readings in this module by truncating the output reaction wheels by a set resolution. This resolution is calculated as a function of the number of clicks per rotation that an analogue sensor might be able to read. If we let be the number of clicks measured during a timestep , then:
where is the speed of the nth reaction wheel, is the number of clicks per rotation and is the remaining clicks that were not accounted for in the previous call of the module. The measured reaction wheel speed is then simply,
This shows that the discretization error is inversely proportional to the sensor resolution and that the error will become more noticeable as wheel speeds approach zero.